Table of Contents

(remove this paragraph once the translation is finished)
Installing an ODROID station in the Bolidozor network
This guide presumes a RMDS02C hardware version of the station with an Odroid-X2 computer.
Installed operating system is Lubuntu 14.04 LTS.
OS image
The downloaded image has to be decompressed and copied onto an eMMC card. The name of the eMMC card can be found after inserting the card into a card reader and seeing the dmesg listing.
xz -d lubuntu_odroid.img.xz sudo dd if=lubuntu_odroid.img of=/dev/sdb bs=1M sync
After copying the image to eMMC card, boot the ODROID and do the other settings directly in it. Default login are as follows:
- Username: odroid
- Password: Bolidozor
Configuring the image
The image on the SD card has to be adjusted in order to function correctly in the network.
There is an account ‘odroid’ with password ‘odroid’ created in Lubuntu. The odroid user is sudoer. Change the password as soon as possible using passwd command.
Change the station’s name in the following files
/etc/hostname /etc/hosts
Chang the MAC address in the following file
/etc/smsc95xx_mac_addr
A new MAC address can be generated directly from the command line, using the following command:
$(echo $FQDN|md5sum|sed 's/^\(..\)\(..\)\(..\)\(..\)\(..\).*$/02:\1:\2:\3:\4:\5/')
In this way a new address is generated based on an absolute domain name of the computer. Therefore it is necessary to first change the station’s name and only afterwards generate a new MAC address for odroid.
Change a time zone (set it to UT) and station’s location
sudo dpkg-reconfigure tzdata
Sometimes it is also necessary to generate a local settings, e.g.:
sudo locale-gen cs_CZ.UTF-8
Finally, expand the ext4 partition using GParted to the full size of the SD card. It is also possible to use odroid-config.
You can find a more detailed information for installations from scratch or in case of difficulties with SW or HW at MLAB wiki. Na předpřipraveném image pro síť Bolidozor by měly být hotové. (?? čo). Then you can follow with launching a detection on a station
Launching a meteor detection on station
Before the first start, you have to copy a config file nazev_binarky.json from directory containing radio-observer source code to a home directory of ODROID user. This file has to be re-named according to the name of the station and it has to be changed according to the location of a folder where the data about detected meteors will be saved.
You can find a description of the Bolidozor network’s config file at radio-observer.
Directories that will contain data about meteors, which the config file refer to, have to already exist. If they do not exist, create them.
Run the detection using the script
~/Bolidozor/netstart.sh
The script can be run directly on the station or it can be redirected, via ssh, to a remote xserver. An example of running ssh with redirecting to xserver of a computer that we kterého provádíme přihlášení (??)
ssh odroid@nazev_stanice -X ~/Bolidozor/netstart.sh
Netstart.sh script description
ulimit -c unlimited ~/Bolidozor/frequency_log.py 1 286.0788& jackd -d alsa -dhw:1& sleep 3 qjackctl& sleep 4 jacktrip -q 8 -r 3 -s& sleep 3 ~/Bolidozor/ODROID3/ODROID3& sleep 3 jack_connect alsa_in:capture_1 system:playback_1 jack_connect alsa_in:capture_2 system:playback_2 jack_connect ODROID3:midi_out system:playback_3
The above-mentioned sample script uses ODROID3 as a station’s name.
ulimit
Ensures saving a core dump if there is an exception in any application.
frequency_log.py
Automatically tunes the radio, so that the zázněj (??) of GRAVES carrier frequency was at 10.6 kHz.
jackd -d alsa -dhw:1&
Launches JACK server with an audio source from card 1. and using alsa driver.
qjackctl
It can be omited. It launches graphic application that helps to see if the server is running and what is connected to what (??).
jacktrip
Launches jacktrip client for transfer of audio data over a network.
~/Bolidozor/jmeno_stanice/jmeno_stanice
Runs the radio-observer - detected meteors begin to be saved into a directory specified in .json config file.
jack_connect
Interconnects all application in case there is a monitoring station connected to the network.
Scripts for data upload
Source codes of data upload scripts can be found at Bolidozor github.
You can also find them on station in ~/git/RMDS-data-uploader. In order to turn the data upload on, you have to change a ~/git/RMDS-data-uploader/config.py config file according to your station’s name and location of files. Then you can run run.py in screen.
screen cd ~/git/RMDS-data-uploader/ ./run.py
A running screen can be left using key shortcut CTRL-A followed by CTRL-D. When set correctly, the config.py uploader sorts the data and uploads them on the central data server space.astro.cz.
Monitoring of detected meteors on PC
You can run a visualisation of detected meteors on any PC connected to LAN. Follow the sequence of commands (that can be placed to netmaster.sh script):
jackd -r -d alsa& sleep 3 qjackctl& sleep 3 ~/git/pysdr/pysdr-waterfall& #~/git/pysdr/pysdr-waterfall -d ~/git/pysdr/detectors/meteor_echo.py& sleep 3 ~/git/pysdr/whistle/whistle -p freqx,-10400:kbfir,41,0,400,100:freqx,400:amplify,200& sleep 3 jack_netsource -H odroid -i2 -I1 -o0 -O0&
jackd
Runs a local JACK server.
qjackctl
A tool for connecting applications in JACK.
pysdr-waterfall
Launches waterfall visualisation. In our case, the OpenGL waterfall display pySDR is installed in ~/git/pysdr directory. Pysdr can be dowloaded to this directory using the following command:
git clone https://github.com/MLAB-project/pysdr
There is also a commented variant of launching the detection of meteors directly in the pysdr in the script.
whistle
Generates sounds of meteors.
jack_netsource
Connects JACK to ODROID via network.
It is convenient to create a netstop.sh batch
killall whistle killall jack_netsource killall jackd killall qjackctl
that will terminate everything. Pysdr-waterfall has to be terminated manually by closing its window.
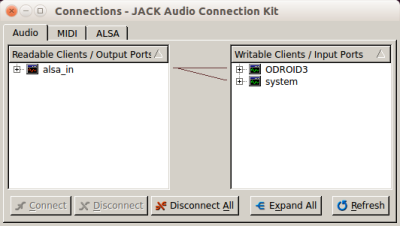
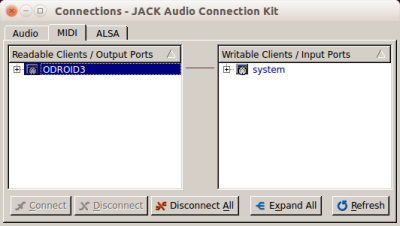
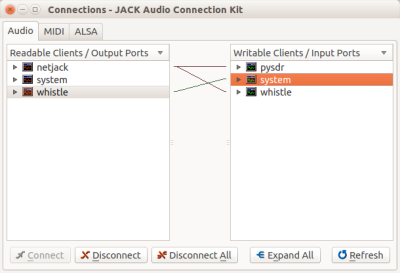
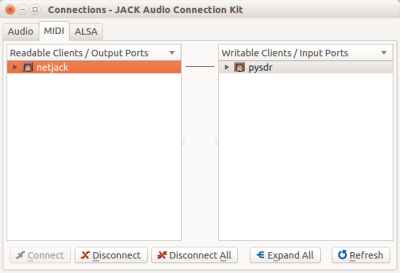
If everything is running, we have to connect everything on both computers using qjackctl or jack_connect.
Connecting the JACK components should look the following way on Odroid
and on PC:
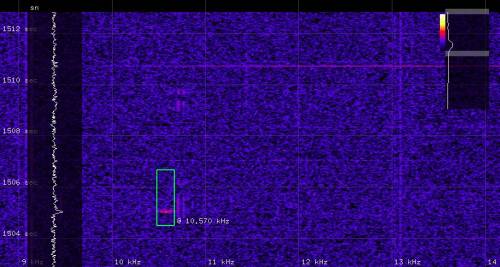
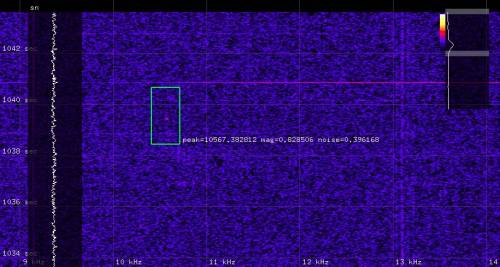
This is how a meteor detected within the sound streem looks like in pysdr
or in radio-observer